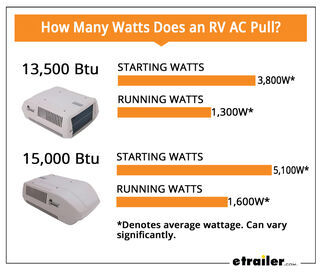
How Many Watts Does A 13500 Btu Air Conditioner Use: Energy Guide
A 13,500 BTU air conditioner typically uses between 1,200 and 1,500 watts. The exact usage depends on efficiency and model.
Air conditioners are crucial for maintaining comfort in hot weather. Understanding their energy consumption is essential for managing electricity bills. A 13,500 BTU unit is a common choice for medium-sized rooms or RVs. Knowing its wattage helps in selecting the right generator or planning energy use.
Energy efficiency varies across models, impacting overall power consumption. Choosing an energy-efficient model can significantly reduce electricity costs. Regular maintenance also ensures optimal performance and energy use. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate wattage information. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions about air conditioning needs.
Introduction To BTU And Watts
When choosing an air conditioner, understanding BTU and watts is crucial. It helps you make the right decision. You need to know how much power your AC uses. This section will explain the basics.
Basic Definitions
BTU stands for British Thermal Unit. It measures energy. One BTU is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. Air conditioners use BTUs to show their cooling capacity.
Watts measure electrical power. One watt is one joule of energy per second. Air conditioners use watts to show how much power they need to run.
Relevance To Air Conditioners
Air conditioners use BTUs and watts to show their performance. A 13,500 BTU air conditioner can cool a large room. But, it needs a specific amount of power to work. Knowing the watts helps you understand the electricity cost.
You can use a simple formula to convert BTU to watts:
- 1 BTU = 0.29307107 watts
So, a 13,500 BTU air conditioner uses:
13,500 BTU 0.29307107 = 3,956.46 wattsNow you know that a 13,500 BTU air conditioner uses about 3,956.46 watts. This information is useful when planning your energy needs.

Credit: blog.ecoflow.com
Calculating Energy Consumption
Understanding how much energy your air conditioner uses is crucial. This helps manage electricity bills. It also promotes energy efficiency. Let’s break down the energy consumption of a 13500 BTU air conditioner.
Btu To Watt Conversion
BTU stands for British Thermal Unit. It measures the cooling power of an air conditioner. To find out the energy usage, we need to convert BTU to watts.
1 BTU is equal to about 0.293 watts. So, a 13500 BTU air conditioner uses:
13500 BTU 0.293 = 3955.5 watts
That means a 13500 BTU air conditioner uses about 3955.5 watts. This number can help you estimate your power needs.
Factors Influencing Power Usage
Several factors affect how much power your air conditioner uses:
- Room Size: Larger rooms need more energy to cool.
- Insulation: Well-insulated rooms retain cool air better.
- Outdoor Temperature: Hotter days require more cooling power.
- Usage Time: Longer use means higher energy consumption.
- Efficiency Rating: Higher efficiency units use less energy.
These factors can change the actual energy use of your air conditioner. Monitoring these can help manage your electricity usage better.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
Understanding the energy efficiency of your air conditioner is crucial. It helps save money and reduce environmental impact. Let’s dive into the key metrics that measure energy efficiency.
Understanding Eer And Seer
The Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) are two important metrics. These ratings tell you how efficiently an air conditioner uses electricity.
EER measures the efficiency of an air conditioner at peak temperatures. The formula is:
EER = BTU / Watts
So, for a 13,500 BTU air conditioner, if it uses 1,500 watts, the EER would be:
EER = 13500 / 1500 = 9
SEER is a more comprehensive metric. It measures the efficiency over an entire cooling season. It accounts for varying temperatures. SEER is calculated as:
SEER = Total BTUs / Total Watt-Hours
A higher EER or SEER rating means better energy efficiency. Always look for these ratings on your air conditioner.
Choosing Energy-efficient Models
Choosing an energy-efficient air conditioner can save a lot of money. Here are some tips:
- Look for Energy Star certified models.
- Check the EER and SEER ratings.
- Consider inverter technology for better efficiency.
Energy-efficient models might cost more upfront. They save money in the long run through lower electricity bills.
Here’s a simple comparison table:
| Model | EER | SEER | Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 9 | 15 | $100 |
| Model B | 10 | 17 | $90 |
| Model C | 11 | 20 | $80 |
Choosing the right model involves looking at both EER and SEER ratings. Always opt for a model that balances cost and efficiency.

Credit: blog.ecoflow.com
Typical Power Usage
Understanding the power usage of a 13500 BTU air conditioner is crucial. It helps you estimate your energy costs and manage your electricity usage efficiently. Let’s break down the typical power consumption of this popular AC unit.
Average Wattage For 13500 Btu Ac
A 13500 BTU air conditioner typically uses between 1000 to 1500 watts. This range can vary based on several factors:
- Energy efficiency of the unit
- Operating conditions like room size and temperature
- Brand and model specifics
Here’s a simple table to illustrate the average wattage:
| Condition | Wattage |
|---|---|
| Optimal Conditions | 1000 – 1200 watts |
| Average Conditions | 1200 – 1350 watts |
| Extreme Conditions | 1350 – 1500 watts |
Comparing Different Brands
Different brands offer different energy efficiency levels. Let’s compare three popular brands:
- Brand A: Known for its high efficiency, uses around 1100 watts.
- Brand B: A mid-range option, typically uses about 1300 watts.
- Brand C: More basic models, consuming up to 1500 watts.
When choosing an air conditioner, consider the energy consumption of different brands. An energy-efficient model can save you money in the long run.
Impact On Electricity Bills
A 13500 BTU air conditioner can keep your room cool. But it can also impact your electricity bill. Understanding how many watts it uses helps you manage costs.
Estimating Monthly Costs
You need to know the air conditioner’s wattage. A 13500 BTU air conditioner uses around 1350 watts per hour. Multiply this by the hours used each day.
For example:
- Usage: 8 hours per day
- Wattage: 1350 watts
- Daily Consumption: 1350 watts x 8 hours = 10800 watts (10.8 kWh)
To find the monthly cost, multiply the daily consumption by 30 days and the cost per kWh. Suppose the cost per kWh is $0.12:
| Daily kWh | Monthly kWh | Cost per kWh | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.8 kWh | 10.8 kWh x 30 = 324 kWh | $0.12 | 324 kWh x $0.12 = $38.88 |
Tips For Reducing Expenses
Reducing air conditioner usage can lower your bills. Here are some tips:
- Use Fans: Fans can help circulate cool air.
- Seal Windows and Doors: This keeps cool air inside.
- Close Blinds: This blocks sunlight and reduces heat.
- Set a Timer: Turn off the AC when you sleep.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean filters for better efficiency.
Environmental Considerations
Understanding the environmental impact of a 13500 BTU air conditioner is crucial. This section delves into the carbon footprint and eco-friendly alternatives of using such appliances.
Carbon Footprint
An air conditioner with 13500 BTU uses a significant amount of energy. This energy consumption translates to a higher carbon footprint. Here is a breakdown of the impact:
- Electricity Usage: A 13500 BTU unit typically uses around 1350 watts per hour.
- CO2 Emissions: Higher electricity usage leads to increased CO2 emissions.
- Environmental Impact: More CO2 emissions contribute to global warming.
Reducing the carbon footprint involves using the air conditioner efficiently. Maintain the unit regularly and set optimal temperatures.
Eco-friendly Alternatives
Consider eco-friendly alternatives to reduce environmental impact. Here are some options:
- Energy-Efficient Models: Choose air conditioners with higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings.
- Smart Thermostats: Use smart thermostats to optimize energy usage.
- Solar-Powered Units: Solar-powered air conditioners can significantly lower electricity consumption.
Implementing these alternatives can reduce energy consumption and minimize the carbon footprint of cooling your home.
Maintenance And Upkeep
To get the best performance from your 13500 BTU air conditioner, regular maintenance is key. Proper upkeep ensures the unit runs efficiently and uses energy effectively. Let’s explore some essential maintenance tips to keep your air conditioner in top shape.
Regular Servicing
Schedule regular servicing for your air conditioner. A technician can check for any issues and fix them. Regular checks ensure the unit is always in good working order.
- Clean or replace filters every month.
- Inspect the coils annually.
- Check the thermostat settings.
These steps help the air conditioner run smoothly. They also help in reducing energy usage.
Energy-saving Tips
Follow some energy-saving tips to reduce your air conditioner’s power consumption. Small changes can make a big difference.
- Set the thermostat to 78°F when home.
- Use a programmable thermostat for better control.
- Seal leaks in doors and windows.
These tips help save energy and reduce electricity bills. Keep your air conditioner running efficiently by following these simple steps.
Future Trends In Air Conditioning
The world of air conditioning is rapidly evolving. New technologies make these systems more efficient and smarter. They aim to save energy and improve comfort. Let’s explore some key trends in air conditioning.
Advancements In Technology
Modern air conditioners use advanced technology. These systems consume less power. A 13500 BTU air conditioner now uses less than 1500 watts. This efficiency helps to lower energy bills.
Inverter technology is one key advancement. This technology allows the compressor to adjust its speed. It provides better temperature control and consumes less energy.
Eco-friendly refrigerants are also gaining popularity. These refrigerants have a lower environmental impact. They help to reduce the carbon footprint of air conditioners.
Smart And Connected Systems
Smart air conditioners are the future. These systems can connect to the internet. You can control them using your smartphone or voice assistants.
Remote control features allow you to adjust settings from anywhere. This ensures your home is always comfortable when you arrive.
Smart systems also offer energy-saving modes. These modes optimize the use of electricity. They ensure the air conditioner runs efficiently.
Some smart air conditioners come with self-diagnosis features. These features can detect issues early. They notify you about maintenance needs. This helps to avoid costly repairs.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Inverter Technology | Better temperature control, less energy use |
| Eco-friendly Refrigerants | Lower environmental impact, reduced carbon footprint |
| Smart Control | Remote settings adjustment, enhanced convenience |
| Energy-saving Modes | Optimized electricity use, efficient operation |
| Self-Diagnosis | Early issue detection, reduced repair costs |
These trends show a promising future for air conditioning. They aim to offer better comfort, savings, and environmental care.
-smart-portable-ac-with-heat,-app-and-voice-control---black/MAP10S1XWBL-3d-Box.jpg/jcr:content/renditions/cq5dam.web.5000.5000.jpeg)
Credit: www.midea.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Size Generator Do I Need To Run My 13500 Btu Air Conditioner?
You need a generator with at least 3,000 to 3,500 watts to run a 13,500 BTU air conditioner efficiently.
How Many Watts Does A 13500 Btu AC Draw?
A 13,500 BTU air conditioner typically draws around 1,200 to 1,500 watts. Check the unit’s specifications for exact details.
Will A 2000 Watt Generator Run My RV AC?
A 2000-watt generator may struggle to run your RV AC, especially during startup. Check your AC’s wattage requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the wattage of a 13500 BTU air conditioner helps manage energy use effectively. This knowledge aids in selecting energy-efficient appliances. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate details. Making informed choices can save you money and reduce your carbon footprint.
Stay energy-conscious and enjoy a comfortable, cool home.