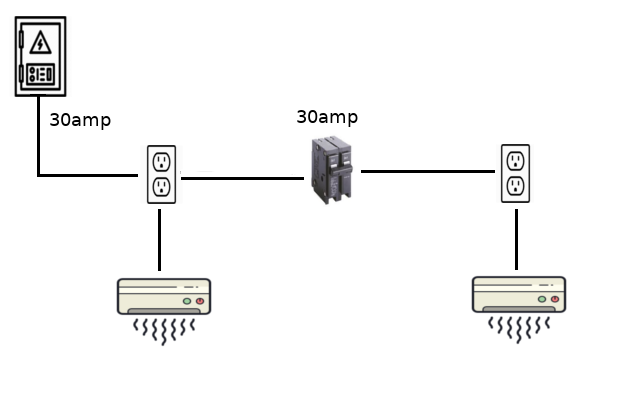
How Many Air Conditioners Can I Run On One Circuit: Essential Guide
You can typically run one air conditioner on a single circuit. Multiple units may overload the circuit, causing a breaker to trip.
Understanding how many air conditioners you can safely run on one circuit is crucial for both safety and efficiency. Most residential circuits are designed to handle a specific load, usually around 15 to 20 amps. Air conditioners, especially larger units, consume a significant amount of power.
Overloading a circuit can lead to electrical issues, including tripped breakers and potential fire hazards. It is always a good practice to consult an electrician to determine the capacity of your existing circuits. Knowing your circuit’s limits ensures your air conditioning system operates smoothly without causing any electrical problems.
Circuit Basics
Understanding the basics of circuits is crucial for safely running air conditioners. Circuits are pathways that carry electricity from your breaker panel to various devices in your home. Air conditioners need a lot of power, so it’s essential to know how many you can run on one circuit.
Types Of Circuits
There are two main types of circuits: dedicated circuits and shared circuits. A dedicated circuit provides power to a single device, like an air conditioner. This type of circuit is the safest and most efficient for high-power devices.
Shared circuits, on the other hand, supply power to multiple devices. These circuits can be overloaded if too many devices are used at once. Overloading can cause tripped breakers or even electrical fires.
Circuit Capacity
Each circuit has a specific capacity, measured in amps. Most residential circuits are either 15 amps or 20 amps. To calculate how many air conditioners you can run, you need to know the power usage of each unit. This is usually listed in watts or BTUs on the device’s label.
Use this formula to find out if your circuit can handle the load:
Amps = Watts / VoltsFor example, if an air conditioner uses 1,500 watts and your circuit is 120 volts:
Amps = 1500 / 120 = 12.5 ampsIf you have a 15-amp circuit, running one air conditioner at 12.5 amps leaves little room for other devices. A 20-amp circuit can handle more but still has limits.
| Circuit Type | Capacity (Amps) | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Circuit | 15 or 20 | One air conditioner |
| Shared Circuit | 15 or 20 | One air conditioner + few low-power devices |
In summary, understanding circuit types and capacities helps determine the number of air conditioners you can run safely. Always prioritize safety and consult a professional if unsure.

Credit: diy.stackexchange.com
Electrical Load Calculation
Understanding the electrical load of your air conditioners is crucial. It helps you know how many units you can safely run on one circuit. Overloading a circuit can cause electrical issues. It can trip circuit breakers or even start fires. This section will guide you through the process. We will break it down into simple steps.
Understanding Watts
Watts measure the electrical power your devices use. It is essential to understand how many watts your air conditioner uses. Most air conditioners have a label or a manual. This will tell you the wattage.
- Small Window AC Units: 500 to 1,500 watts
- Medium Window AC Units: 1,500 to 2,500 watts
- Large Window AC Units: 2,500 to 3,500 watts
Calculating Total Load
To calculate the total load, sum the wattage of all air conditioners. Ensure the total does not exceed the circuit’s capacity. Most household circuits are 15 or 20 amps.
Use this formula to calculate the load:
Total Load (Watts) = Number of Units × Wattage of Each Unit
For example, if you have two small units:
Total Load = 2 × 1,000 = 2,000 watts
Now, convert watts to amps:
Amps = Watts / Voltage
Assume your voltage is 120V:
Amps = 2,000 / 120 = 16.67 amps
Check if this is below your circuit’s capacity. A 15-amp circuit cannot handle 16.67 amps. You would need a 20-amp circuit. Always ensure to stay within safe limits.
Air Conditioner Power Requirements
Understanding your air conditioner power requirements is essential. It helps you decide how many units can safely run on one circuit. Knowing the power needs prevents electrical overloads and ensures efficient operation.
Btu To Watts Conversion
Air conditioner power is measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units). To find out the electrical power needed, convert BTUs to watts.
- 1 BTU = 0.293 watts
- Example: A 10,000 BTU unit = 10,000 x 0.293 = 2,930 watts
Use this conversion to calculate your air conditioner’s power consumption. This helps you determine how many units one circuit can handle.
Average Power Consumption
Different air conditioners have different power needs. Here are some average power consumption figures:
| BTUs | Watts | Amps |
|---|---|---|
| 5,000 BTU | 1,465 watts | 12.2 amps |
| 10,000 BTU | 2,930 watts | 24.4 amps |
| 15,000 BTU | 4,395 watts | 36.6 amps |
Most homes have circuits that can handle 15-20 amps. To avoid overloads, ensure the total amps of air conditioners on one circuit is within this range.
For example, a 15-amp circuit can handle one 5,000 BTU unit or half of a 10,000 BTU unit. Always check your circuit’s capacity before adding more air conditioners.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Single Circuit Limitations
Understanding the limitations of a single circuit is crucial. It ensures safety and efficiency in your home. Running multiple air conditioners on one circuit can be tricky. Let’s explore the key factors involved.
Safety Concerns
Safety should always be your top priority. Overloading a circuit can cause serious issues. These include short circuits and fire hazards. Make sure the total load does not exceed the circuit’s capacity. Always check the wattage of each air conditioner.
For example, if each air conditioner uses 1500 watts and your circuit supports 3000 watts, you can run two units. But this leaves no room for other appliances. This increases the risk of overloading the circuit.
Breaker Specifications
Circuit breakers play a vital role in managing your electrical load. Each breaker has a specific amperage rating. This rating tells you how much current the circuit can handle. Common ratings are 15-20 amps.
| Breaker Rating (Amps) | Maximum Wattage (Watts) |
|---|---|
| 15 | 1800 |
| 20 | 2400 |
Use the formula: Wattage = Voltage x Amperage. For a 120V circuit, a 15-amp breaker supports 1800 watts. A 20-amp breaker supports 2400 watts. Ensure your air conditioners’ total wattage does not exceed these limits.
Some air conditioners have a higher starting wattage. This can momentarily exceed the breaker’s capacity. Always check the specifications of your air conditioners before using them on a single circuit.
Multiple Ac Units On One Circuit
Understanding how many air conditioners can run on one circuit is essential. It helps prevent electrical hazards and ensures efficiency. This section explores the possibility of running multiple AC units on one circuit.
Possible Configurations
Several configurations can run multiple AC units on one circuit. Here are some common setups:
- Single 15-amp Circuit: May run one small AC unit.
- Single 20-amp Circuit: Can handle one medium AC unit.
- Dedicated Circuit: Preferable for large AC units.
The table below shows the possible configurations:
| Circuit Type | Number of AC Units |
|---|---|
| 15-amp | 1 small unit |
| 20-amp | 1 medium unit |
| Dedicated | 1 large unit |
Practical Considerations
Running multiple AC units on one circuit requires careful planning. Here are some factors to consider:
- Circuit Capacity: Ensure the circuit can handle the load.
- Unit Size: Larger units need more power.
- Safety: Avoid overloading the circuit.
Calculating the total wattage of the AC units is crucial. Each unit has a specific power rating, usually in watts or amps. Ensure the combined wattage does not exceed the circuit’s capacity.
For example, a 15-amp circuit can handle up to 1,800 watts. If two units use 900 watts each, they can run on the same circuit.
Remember: Always consult a qualified electrician before making changes. Safety should always be the top priority.

Credit: www.circuitbreakerwholesale.com
Upgrading Your Electrical System
Running multiple air conditioners on one circuit can be risky. Your electrical system may not handle the load. Upgrading your system ensures safety and efficiency.
When To Upgrade
Knowing when to upgrade is crucial. Here are some signs:
- Frequent circuit breaker trips
- Dim or flickering lights
- Unusual noises from outlets
- Old or outdated wiring
If you notice these signs, consider an upgrade. Your home’s safety depends on a reliable electrical system.
Professional Installation
Hire a professional for the installation. They have the skills and tools needed.
Professionals follow safety codes. They ensure your system can handle multiple air conditioners. This prevents potential hazards like electrical fires.
Here’s a comparison of DIY vs. Professional Installation:
| DIY | Professional |
|---|---|
| Risk of mistakes | High expertise |
| May not meet safety codes | Meets all safety regulations |
| Time-consuming | Efficient and quick |
Opt for a professional installation to ensure safety and efficiency. Upgrading your electrical system is an investment in your home’s future.
Energy Efficiency Tips
Running multiple air conditioners on one circuit can be tricky. Energy efficiency can help reduce the strain on your electrical system. Below are some tips to ensure your air conditioners run efficiently and safely.
Choosing Efficient Models
Choose energy-efficient air conditioner models. Look for units with the Energy Star label. These models use less power and provide better cooling.
- Check the SEER rating. Higher SEER means better efficiency.
- Pick units with a programmable thermostat. It saves energy when you are away.
- Ensure the unit size matches the room size. An oversized unit wastes energy.
Proper Maintenance
Maintaining your air conditioner ensures it runs efficiently. Follow these steps:
- Clean or replace filters every month. Dirty filters reduce airflow.
- Check the coils yearly. Clean coils help with heat absorption.
- Inspect the fins. Straighten bent fins to maintain airflow.
Schedule a professional maintenance check once a year. This ensures all parts are working well.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
Running multiple air conditioners on one circuit can cause problems. Understanding these issues helps keep your home safe and cool. This section covers common problems, DIY fixes, and when to call a pro.
Common Problems
Several issues can arise when running many air conditioners on one circuit:
- Overloading: Too many devices can trip the circuit breaker.
- Overheating: Wires may overheat, causing a fire risk.
- Voltage Drops: Multiple units may cause voltage drops, affecting performance.
Diy Fixes And When To Call A Pro
Some problems you can fix yourself, while others need a professional:
DIY Fixes
- Check Breakers: Make sure breakers are not tripped.
- Inspect Wires: Look for damaged or loose wires.
- Redistribute Load: Move some devices to another circuit.
When to Call a Pro
Some issues require professional help:
- Frequent Breaker Trips: If breakers trip often, call an electrician.
- Burning Smell: A burning smell means wires may be overheating.
- Sparking Outlets: Sparks from outlets are dangerous and need expert help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Run 2 Air Conditioners At The Same Time?
Yes, you can run two air conditioners at the same time. Ensure your electrical system can handle the load. Check your circuit breaker capacity to avoid overloading.
Can You Plug Two Ac Units Into One Outlet?
No, you shouldn’t plug two AC units into one outlet. It can overload the circuit, causing electrical hazards.
How Many Acs Can I Run In My House?
The number of ACs you can run depends on your home’s electrical capacity. Typically, a standard home can handle 2-3 units. Always consult an electrician for accurate assessment.
Conclusion
Understanding your circuit’s capacity ensures safe air conditioner usage. Always check your circuit’s limit and avoid overloading. Proper planning prevents electrical issues and keeps your home comfortable. Consult a professional if unsure about your setup. Stay safe and enjoy efficient cooling without risking damage to your electrical system.